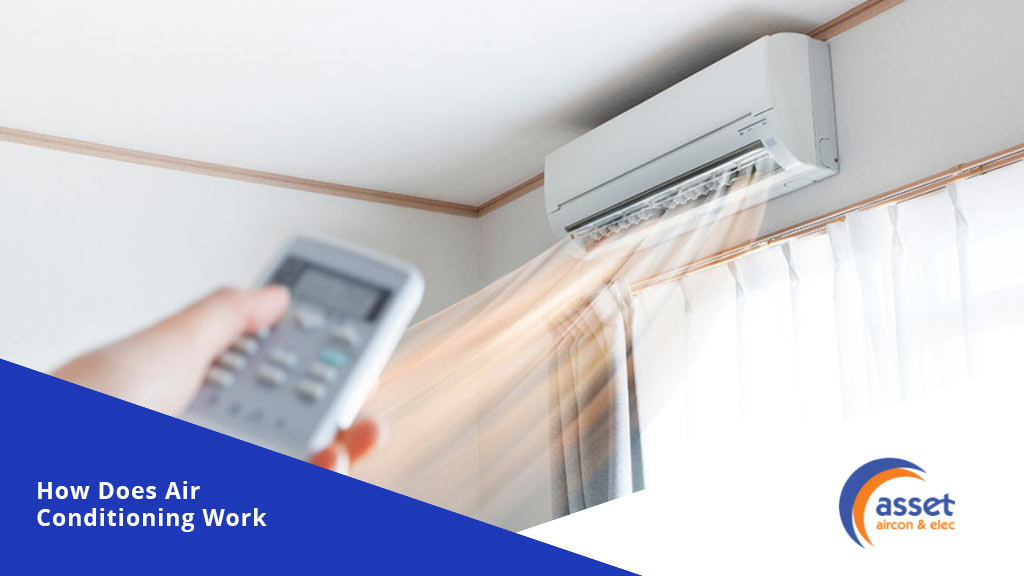
Air conditioners are often associated with making room conditions cooler. In reality, the actual science behind cooling down a room using an air conditioning unit is not merely blasting cold air inwards but actually involves a strategic transfer of heat from inside the house or building directed towards the outside. So how does an air conditioner work?
An air conditioning system uses a refrigerant that is contained within that absorbs the excess heat from a room. Then it is pumped out through the series of pipes that goes towards the outside coil. A fan or a blower pushes the air over this heated coil that contains the refrigerant, allowing the transfer of the heat towards the outdoor air.
Once cooled, the refrigerant will flow back towards the indoor unit while the fans push the cooler air into the room or indoor space. Starting the process all over again, which repeats in continuous cycles. When the heat gets removed, only cool air remains, the fans will then blow this back into the room that cools down the indoor area even further.
On the other hand, how an air conditioner works when used in heating a room is exactly the same process that will run and cycle in reverse. That is why it is called reverse cycle technology.